Technical Specifications
Chemical Composition
- Carbon (C): ≤ 0.07% – Limits carbide formation and retains toughness.
- Silicon (Si): ≤ 1.00% – Adds strength and supports alloy stability.
- Manganese (Mn): ≤ 1.00% – Enhances toughness.
- Phosphorus (P): ≤ 0.04% – Improves cleanliness and reduces brittleness.
- Sulfur (S): ≤ 0.03% – Maintains weldability.
- Chromium (Cr): 15.0‑17.5% – Provides corrosion resistance and strength.
- Nickel (Ni): 3.0‑5.0% – Enhances toughness and stabilizes microstructure.
- Copper (Cu): 3.0‑5.0% – Key element in precipitation hardening response.
- Niobium + Tantalum (Nb+Ta): 0.15‑0.45% – Strengthens matrix and improves aging response.
- Iron (Fe): Balance – Main matrix element.
Treatment
- Solution Annealed (Condition A): Heated to ~1038°C (1900°F) for ~½ hour, then air or oil cooled to refine structure.
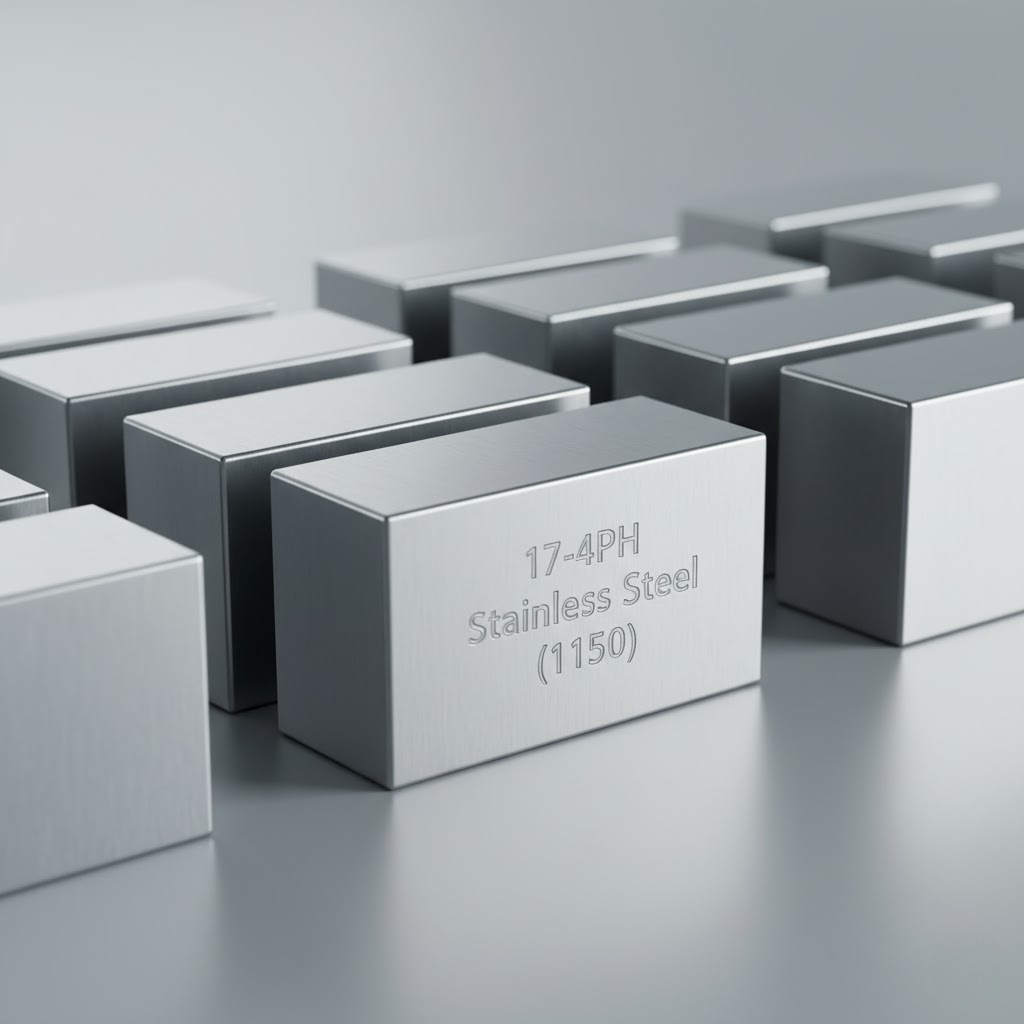
- Precipitation Hardening (H1150): Aged at ~621°C (1150°F) for ~4 hours then air cooled to achieve high strength (~135‑170 ksi UTS).
- Post‐Machining Stress Relief: After aging, the component may be stress relieved or cold worked to minimize residual stresses and ensure dimensional stability.
- Fabrication Advice: Material can be welded in Condition A; the welds should then be aged. For best corrosion resistance in marine environments, use H1150 or above.